The climate change challenge requires all industries to rethink their business practices, and for manufacturers this involves incorporating sustainable manufacturing best practices into their business strategy and management system.
In a recent interview, Helen Fu, ESG & Sustainability Expert, outlined some of the main environmental issues in the manufacturing sector, key areas that manufacturers should be managing, and how the Environmental Sustainability TRACC supports this journey.
Increasing pressure from governments, communities, customers and employees has persuaded many manufacturers to investigate how to incorporate sustainable practices into their business strategies and objectives. They have been looking for more sustainable and energy efficient solutions that respond to regulatory constraints, enhance their reputation, build public trust, increase operational efficiency, provide opportunities for competitive advantage and, ultimately, have a positive impact on communities, the economy and the environment.
In a recent interview, ESG & Sustainability Expert and CCi sustainability strategist and SME for Environmental Sustainability, Helen Fu, talked to us about environmental sustainability (ES) and, more specifically, sustainable manufacturing. Helen has vast experience in corporate ESG & sustainability management, carbon neutrality management, and supply chain sustainability development. She was the Environmental Sustainability TRACC best practice deployment task leader at Mengniu Dairy (see case study summary at the end of this blog) , the first Chinese company to integrate environmental sustainability best practices into its management system, which aims to promote the sustainable development of China’s dairy industry, and the first company to win the sustainability award, the Golden Key Honor Award.
-
What is the environmental impact created by traditional manufacturing?
Traditional manufacturing has a large, negative impact on our environment. During manufacturing processes, hazardous gas emissions, waste and wastewater discharge are common outputs. But to mitigate the impact, manufacturers need to pay special attention to these issues, and manage the emission, waste and discharge properly to ensure substances don’t enter the environment directly.
-
Why should manufacturers pay more attention to environmental sustainability topics?
Global warming is happening faster than many people realized and climate change calls for action. The Greenhouse Gas (GHG) Protocol categorizes GHG emissions into three groups or “Scopes”. Scope 1 covers direct emissions from owned or controlled sources. Scope 2 covers indirect emissions from the generation of purchased electricity, steam, heating and cooling consumed by the reporting company. Scope 3 refers to all other indirect emissions.
Assessing and addressing the Scope 3 GHG emissions created by traditional manufacturing is crucial. Stakeholders are expecting companies to be more transparent about disclosing this information and are monitoring the company’s environmental sustainability performance. Decarbonization and how to map out the current status of the full scope GHG emissions are important topics to explore.
-
What are the key environmental issues manufacturers need to be aware of?
It is important for manufacturers to understand stakeholders’ expectations. For regulators, environmental legal compliance is a fundamental requirement. For investors, transparent environmental information disclosure is important, and they would like to see continuous improvement.
An ESG rating such as MSCI helps manufacturers to see the whole picture of their environmental, social and governance performance. When it comes to the environmental score, the key issues fall under the categories of climate change (carbon emissions, product carbon footprint, financing environmental impact, climate change vulnerability), natural capital (water sourcing, biodiversity and land use, raw material sourcing), pollution and waste (toxic emissions and waste, packaging material and waste, electronic waste), and environmental opportunities (clean technology, green building, renewable energy). (Source: MSCI ESG Ratings Methodology, Executive Summary, MSCI ESG Research, November 2020)
-
What is sustainable manufacturing? Can you provide some examples and key benefits for organizations and the communities in which they operate?
The term ‘‘Sustainable Manufacturing’’ means the “creation of manufactured products through economically-sound processes that minimize[s] negative environmental impacts while conserving energy.” (www.epa.gov/., 2020). Therefore, it refers to products being created with less GHG emissions, less water consumption, less waste and less wastewater discharge that pollute the planet.
Here are some examples of sustainable manufacturing (also see the Results section of the Mengniu case study summary below ) and the benefits for organizations and their communities:
| Examples: |
|
|
| Benefits: |
|
-
What does the Environmental Sustainability (ES) TRACC cover?
The Environmental Sustainability TRACC is designed to support the corporate sustainability strategy by guiding operations in the implementation of environmental best practices. The TRACC enables the operation to identify and prioritize the most pertinent environmental issues (also see the Solution section in the Mengniu case study summary below), which may include energy and GHG emissions, water and wastewater, waste (materials to be disposed of for which the site has no further use), air pollution and Substances of Concern (SOC).
The scope of the TRACC expands from an initial focus on internal operations and priority issues, to work with secondary priority issues and the organization’s value chains to significantly improve operational as well as organizational environmental performance, ultimately influencing change in the industry.
The 6 levels of strategic focus
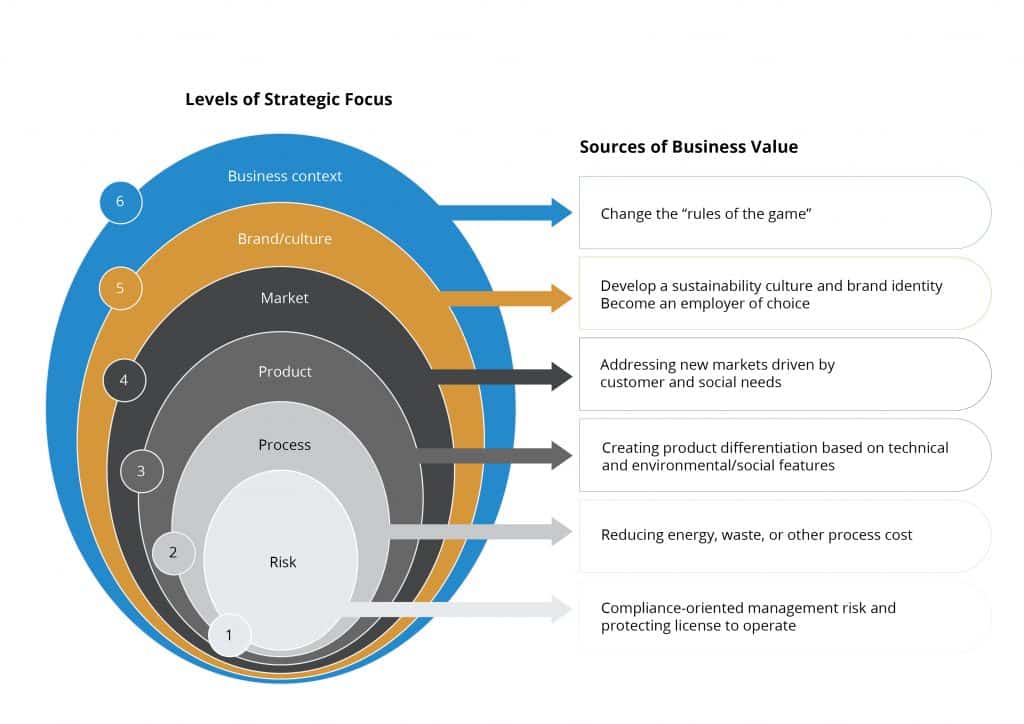
9 themes
The ES TRACC has been divided into nine themes that create a clear, coordinated and logically sequenced best practice implementation road map. A progress chart reflects the maturity of an area being assessed, across five stages, for each of the themes.
-
How does the ES TRACC help manage manufacturing’s environmental sustainability performance and encourage continuous improvement?
The ES TRACC helps manufacturers understand the critical environmental sustainability issues as outlined in the image below.
The 7 critical environmental sustainability issues
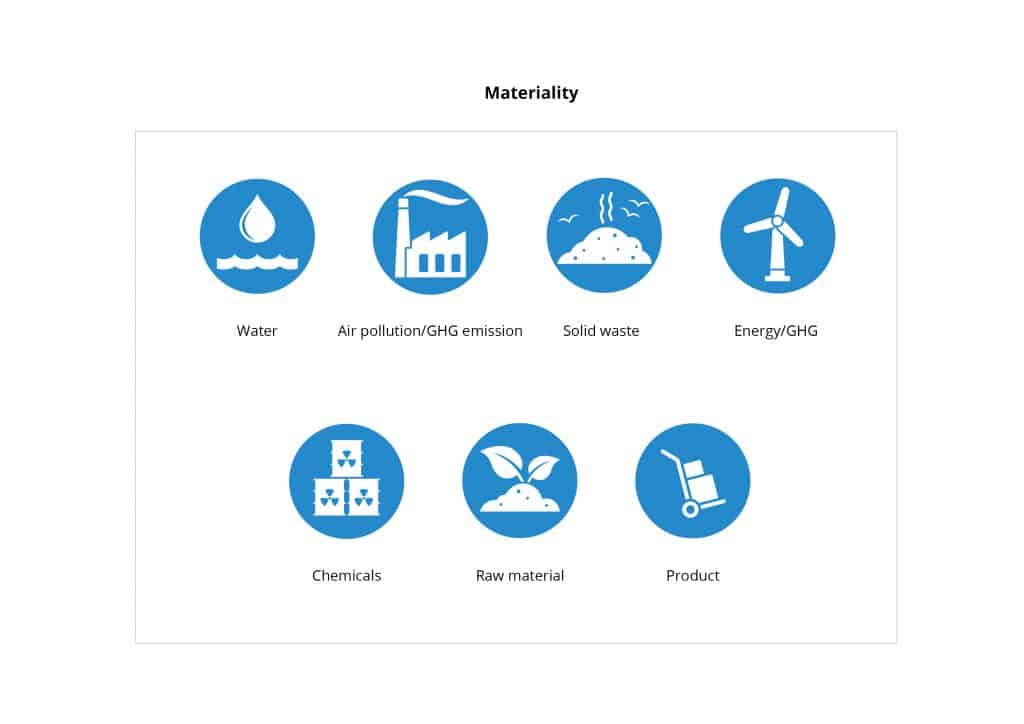
The TRACC’s five stages of maturity enables an organization to pursue the road to excellence in manageable stages – thereby continually improving. It takes an organization from reactive to proactive, innovative and collaborative.
-
What value does the ES TRACC create for brand/supply chain management?
The ES TRACC creates a mature and complete framework. It supports companies in meeting legislative requirements, understanding customers’ expectations about environment sustainability, creating a better environment, minimizing the negative impact on the environment, and reducing operational costs, and contributes toward risk management and competitive advantage development by creating a compliant and sustainable supply chain.
-
What advice would you give to manufacturers starting out on the road to sustainable manufacturing? Where should they begin?
The manufacturing process is a large contributor of GHG emissions. Manufacturers therefore need to pay special attention to environmental sustainability issues. In addition, sustainable manufacturing plays an important part in meeting stakeholder expectations and maintaining a competitive advantage. The ES TRACC can help manufacturers by conducting a maturity assessment of your current manufacturing processes, an ES ‘‘health check’’, and providing a gap analysis – the gap between the status and ES best practice. The ES TRACC then supports the organization’s journey to close these gaps.
The United Nation’s universal call to action to end poverty, protect the environment and ensure prosperity by 2030 prompted Mengniu Dairy in China to introduce the GOAL system.
Here is a summary of this Mengniu Dairy case study which illustrates how the ES TRACC as well as CCi’s consulting services supported Mengniu during their ES improvement journey:
Summary of the Mengniu Dairy case study
In May 2019, a group of Beijing Shijia Hutong Primary School students, their teachers and parents visited Mengniu Fresh Dairy Products business division, and impressed Mengniu representatives with their solutions such as the eco-friendly ‘‘new straw made of chocolate’’ designs.
| Challenge | Mengniu Dairy realized consumer preferences were changing fast. Their challenges were to combine sustainable development with their business and improvement strategy, to sell the concept internally as a lifestyle, establish a responsible supply chain, and pass it on through products and brands to consumers. | |
| Solution | The company decided to roll out CCi’s Environmental Sustainability (ES) TRACC, signaling the birth of the Green Operation and Life (GOAL) system which focuses on key environmental concerns related to the company’s operations, and promotes a positive culture and behavior. Mengniu Dairy also published their sustainable development strategy with the core promise to protect the common health of humankind and the planet. The strategy is based on the 17 Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) adopted by the United Nations in 2015.Mengniu Dairy’s ES team developed three levels to implement the GOAL system:
Level 1: Connect the modules of the GOAL system to each management function Level 2: Focus on two pilot factories Level 3: Focus on non-ES pilot factories “The TRACC-driven GOAL system is proving to be the boost we needed to achieve our 2025 new Mengniu targets.”
– Luo Jianbing, Operation Performance Director of Mengniu Fresh Fermented Dairy Products |
|
| Results | The first Golden Key Honor Award for Mengniu Dairy’s GOAL system in 2020, the second Golden Key Excellence Award for ‘‘Fighting against food waste through cooperation with food bank’’ in 2021The carbon neutral best practice case for ‘‘Fighting against food waste through cooperation with food bank’’ in 2021
Golden Apple Award from the China Sustainable Plastics Association (CSPA) for replacing carton boxes with recycled polypropylene (PP) plastic boxes in 2019, for the GOAL system implementation in Qingyuan pilot plant in 2021 The preventive milk loss map won second prize in the 4th ‘‘Puhua Smart Cup’’ Benchmark Lean Improvement Competition in 2020, second BP on pasteurization milk loss improvement won first prize in the 5th ‘‘Puhua Smart Cup’’ in 2021 Significant improvements in resource utilization and environmental performance, including reductions in milk and other raw and processed material loss, water consumption, energy efficiency and carbon emissions Significant improvements in environmental management system building (compliance and competency) and sustainability system building (awareness and competency, stakeholders’ connection and co-creations) |
Contact us today if you’d like to learn more about how the ES TRACC can support you to achieve sustainable manufacturing.
